A climate justice approach that’s as inclusive as it is effective
Systems Science
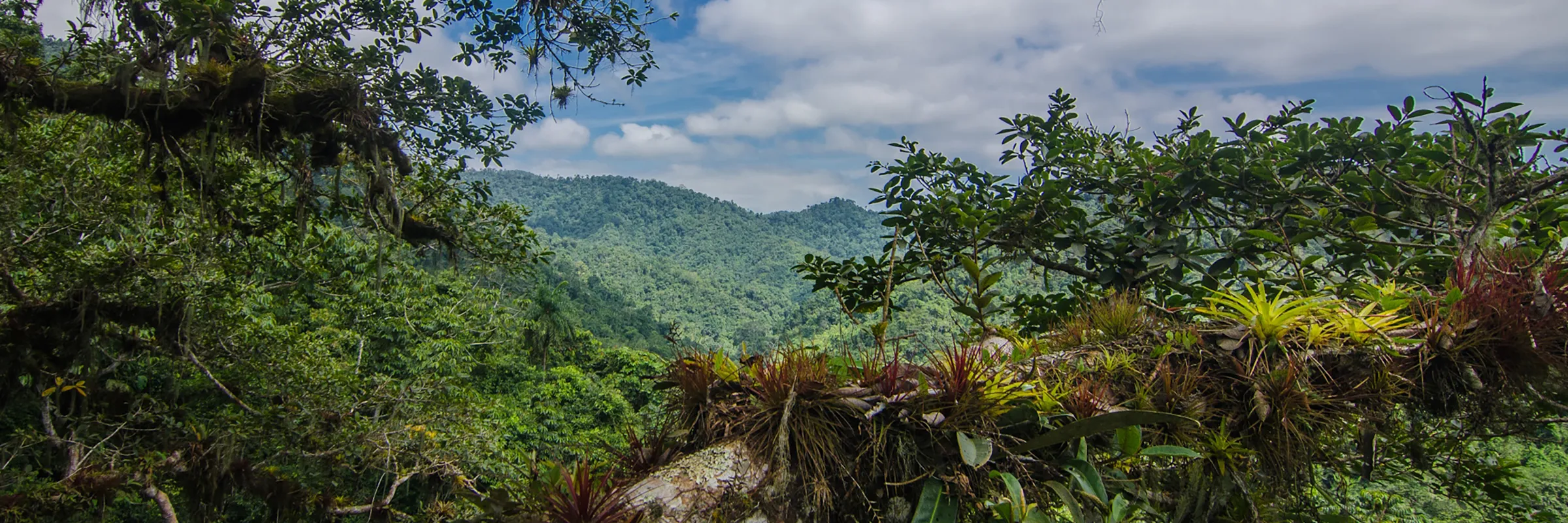
Tackling climate change holistically for lasting impacts
Climate change is more than just an environmental issue. It’s deeply tied to economic activities, policies, and social structures. By understanding how these factors interact and influence one another, we can design solutions that address the root causes.
Equity Approach
Putting fairness at the forefront of decision making
The impacts of climate change are not distributed equally. Indigenous Peoples and marginalized communities are often affected most despite contributing to the problem least. Climate actions must address social inequalities in addition to mitigating climate change.
The Carbon Justice Standard sets a new precedent for integrated, just, and equitable climate action.
Our core principles
Every certified project is designed, developed, and evaluated according to the following principles.
1. Integrated Benefit Assessment
Go beyond carbon reduction to include biodiversity preservation and social benefits
Each project under the CJ Standard is designed to deliver benefits across all three areas. Climate action is not siloed but integrated into a broader context of sustainability and equity.
2. Community-Centric Approach
Empower Indigenous Peoples and local communities by co-designing projects
Projects incorporate the knowledge and consent of IP & LCs and actively support their self-determination and cultural practices. Initiatives not only respect the rights and cultures of IP & LCs but also acknowledge their intrinsic value as custodians of the planet's most vital carbon sinks.
3. TARGETED DEFORESTATION INTERVENTIONS
Combat the main drivers of deforestation and degradation
Projects must address the root causes of climate change, such as unsustainable agricultural expansion and extractive industries. To combat these drivers, projects must employ targeted strategies to address the systemic factors contributing to forest loss, ensuring that climate projects have a lasting impact.
4. Transparent Governance
Conduct projects with integrity, accountability, and adaptability
By adhering to transparent governance, projects under the CJ Standard can build trust with stakeholders, particularly IP & LCs, ensuring that climate action is not only effective but also just and equitable.
5. EQUITABLE ECONOMIC DISTRIBUTION
Ensure fair compensation for the stewardship roles of Indigenous People and local communities
Economic benefits from climate projects must foster tangible improvements in the quality of life for IP & LCs. This involves setting carbon prices that reflect the true social cost of carbon. Ultimately, the community decides how best to spend the funding as long as it is supportive of the project goals.
6. High Environmental Integrity
Capture the true impact of climate interventions over time
Recognizing the evolving nature of ecosystems, CJ Standard projects use dynamic baselines that reflect current environmental conditions. Our view of additionality rewards ongoing conservation efforts by IP & LCs and does not penalize them for past sustainable practices.
These CJ Standard core principles are the foundation for our approach and shape our project life-cycle. Explore how to design a project.
Flexible models for meaningful climate action
The Carbon Justice Standard offers two distinct approaches to ensure your investment aligns with your goals while driving real impact.
Carbon offset model
Rigorously analyzed carbon offsets allow you to invest in projects that reduce emissions and apply toward carbon neutrality claims.
Climate contribution model
Take action beyond your operational footprint by investing in critical climate projects without claiming carbon offsets.

Dive deeper with the CJ Standard white paper
For a deeper understanding of the CJ Standard principles and how they benefit communities, you can request our white paper below.